Table Of Contents
What Is Investment Banking?
Investment banking refers to financial services concerning large and complex transactions, investment advice, capital raising, risk management, and other financial solutions. Some investment banks are universal banks, acting as a conglomerate of commercial and investment banking services simultaneously.
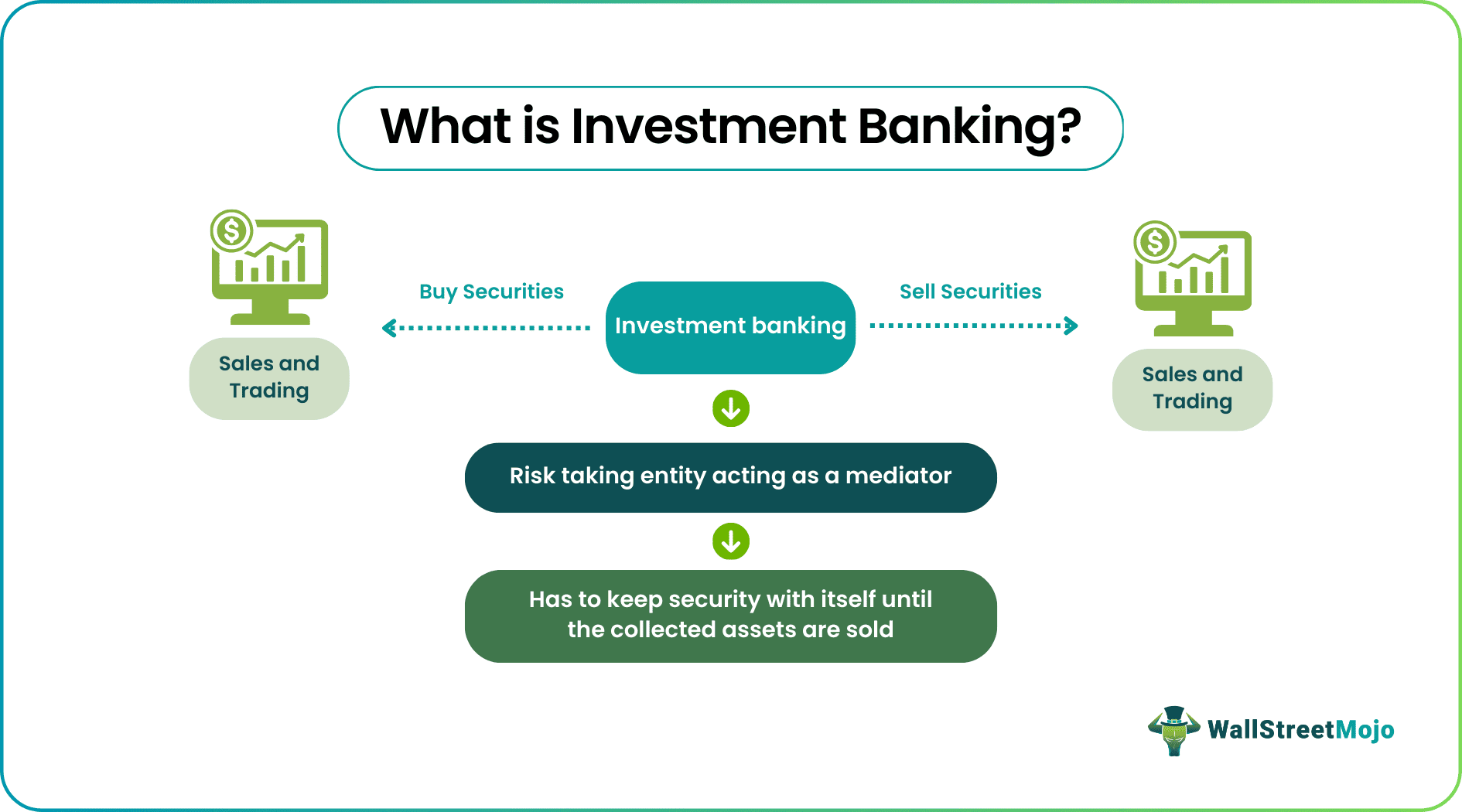
An investment banking entity is a bridge between businesses seeking capital and investors, ready to use the funds to reap profitable returns. These banks purchase securities from different entities and sell them to interested investors, keeping the market active and efficient. However, the reputation of the banks plays a great role in attracting more and more investors to a project.
Key Takeaways
- Investment banking is a division of financial corporations that creates new debt and security instruments, underwrites IPO processes,
- offers advice on mergers or acquisitions, and helps high-net-worth individuals and banks facilitate high-value investments.
- Investment banks are a mediator between businesses and investors, carrying all the risks and acting as a shield to both parties.
- It helps businesses build capital by raising funds from investors based on the years of reputation that they have built.
- The services offered to customers depend on the type of investment bank, be it bulge bracket, middle market, or boutique bank.
Investment Banking Explained
Investment banking emerged as a concept in the early 19th century when commercial banks dealt with the investment banking requirements of various entities. However, the emergence of the American Civil War made financier Jay Cooke start the first investment bank to fund the US war efforts.
The US government became the first client and started issuing bonds through investment banks to interested investors. The funds raised help the authorities fund their fundamental requirements and pay off investors with a share of the profit earned once the projects were accomplished.
The bonds served as an IOU, a payback promise in writing. Per this, the investment banks bought the bonds and sold the same to investors for profits. The banks continue doing the same even today. However, these banks attract clients and investors based on the reputation they have built over a period. Their history plays a vital role in making the stakeholders trust the businesses they collaborate with.
Types
The banking services are classified based on the types of banks providing them. The first one is the bulge bracket bank which forms the largest part of the investment banking field. They operate around the world and offer investment and advisory services efficiently.
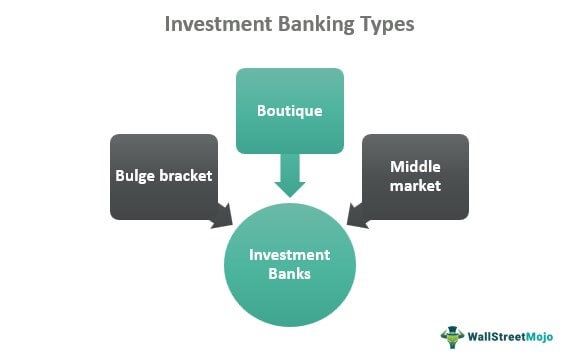
Middle-market banks are the next on the list, which are comparatively smaller and operate on a limited scale. On the contrary, boutique banks, the third on the list, segment the customers before offering their services. These banks are for elite, regional, and industry-specific clients. While the elite banks take care of the major asset management, mergers and acquisitions, and other bigger deals, the rest two are restricted to offering services to specific regions and industries.
Functions
Trading is one of the least talked-about functions of investment banking. The salespeople work as analysts and approach investors with investing opportunities. In turn, traders take up trades and convey to the client when to consider entering and exiting positions.
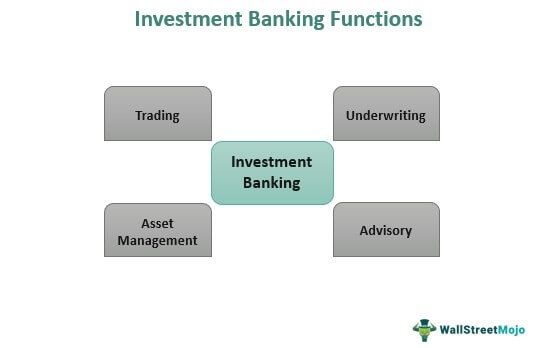
Underwriting, the next one, makes these banks buy assets and securities having monetary value and sell the same to investors. The parties get involved in such deals as they have a middleman to take care of the risks and become their shield against the losses incurred. This makes the banks keep the securities to themselves until sold as they have already paid the clients for them.
Investment banks offer asset management services through which it helps clients manage their investment funds. The assets are managed using individual accounts for stocks, fixed-income stocks, derivatives, etc.
One of the most vital services of these banking institutions is their advisory functions. They help clients with valuable advice related to major business dealings, especially M&A. In addition, the ones into investment banking jobs help buyers and sellers of entities intending to merge with or acquire/being acquired by businesses.
Examples
The examples below help us understand the investment banking meaning and its functions better:
Example #1
Stella sets up a start-up. However, she is still searching for investors to raise capital. Being a novice in the market, she connects with an investment banking firm, A, which has an established history of helping businesses to operate well. The firm buys the securities from Stella and sells the same to investors to raise funds.
Example #2
Being the risk-taking middleman, the investment bankers played a crucial role in the Subprime Mortgage Crisis of 2008. As the Federal Reserve increased the bank's liquidity, it lowered the funds' rate, leading to commercial banks offering home loans without any strict criteria. With more and more home seekers taking up loans, commercial banks started selling the old financial obligations to investment banks, selling them to investors, and making them appear as secured investments. This allowed them to offer more home loans over time.
This cycle continued for consecutive years until the interest rates started rising, causing borrowers to default and affecting the banking sector. Though the investment bankers were found responsible for creating the bubble that burst, causing the collapse of the American economy, the same entities helped build it again with a far better and more stable infrastructure and economic foundations. Hence, even though it's a complicated field, investment banking holds a bright future ahead.
Example #3
According to a report published on May 20, 2025, the co-chief executive officer of JPMorgan’s commercial & investment bank expects a significant drop in investment banking fees, which, in turn, will impact the revenue. The reason behind this drop in fees will be the uncertainty in the economic environment. That said, JPMorgan is still optimistic regarding its trading revenue. Some of the key factors influencing economic uncertainty include tariff issues, inflationary concerns, and geopolitical tensions. Despite such challenges, the chief executive officer of JPMorgan remains optimistic regarding the financial stability of the company.
Regulation
With its evolution, two types of banks started – investment banks and commercial banks. While commercial banks dealt with the daily deposits and withdrawals and other simple banking services, investment banks were responsible for bigger financial affairs, including mergers and acquisitions (M&A), underwriting, etc. Then, some conglomerates acted as both investment and commercial banks and came to be referred to as universal banks.
When the functions collided, the universal banks had details of investors, who were also borrowers, which made it convenient for them to sell risky positions out of bias. These concerns made the authorities introduce the US Glass-Steagall Act of 1933, which prohibited commercial banks from offering investment banking facilities. In 1999, however, the act was repealed and replaced with the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, allowing commercial banks to offer investment banking services again. This led to mergers, forming global conglomerates like HSBC, J.P. Morgan Chase, etc., while some, like Goldman Sachs, and Morgan Stanley, preferred to function as pure investment banks.
Investment Banking Skills
Working in an investment bank efficiently requires one to have certain skills. Let us find out what they are.
- Book-Building: This process involves figuring out the pricing for initial public offerings or IPOs on the basis of the bids placed by investors.
- Relationship Management: This involves closing deals with clients and ensuring their satisfaction with the service offered.
- Business Valuation: Investment bankers need to know how they can use different valuation techniques to obtain a company’s accurate valuation.
- Negotiation: This is a vital skill required for investment bankers to maximize value creation for clients.
- Financial Modeling: Investment bankers must understand how to use Excel to create different types of financial models, like 3-statement models. Leveraged buyout or LBO models. If you wish to develop a practical understanding of financial modeling and other key techniques used in investment banking, like valuation, enrolling in the Investment Banking Mastery Program (IBMP) can be extremely helpful.
Investment Banking vs. Commercial Banking
Individuals new to finance often have confusion regarding the meaning and purpose of investment and commercial banking. So, the table below highlights the key differences between the two types of financial services to eliminate their confusion.
| Investment Banking | Commercial Banking |
|---|---|
| The primary services of investment banks include offering financial advisory services, helping companies raise capital, and facilitating investing and trading. | A commercial bank accepts deposits from individuals and organizations and offers loans. |
| Generally, investment banks participate in activities that are associated with a higher degree of financial risk. | The risk associated with commercial banking activities is comparatively lower. |
| The clients of investment banks primarily comprise the general public | Investment banks’ clients comprise high-net-worth individuals, governments, and corporations. |
| Commercial banks generate income by earning interest on loans and imposing fees. | Investment banks generate income via underwriting services, asset management fees, trading profits, and advisory fees. |
Investment Banking vs. Private Equity
If individuals have doubts about how investment banking and private equity differ, they can refer to the table below:
| Investment Banking | Private Equity |
|---|---|
| Investment banks generate income via different channels, like mergers and acquisitions or M&As, underwriting services, and research services. | In private equity, the generation of revenue takes place via capital appreciation, leverage, management fees, performance fees, exit, dividend distributions, and leverage. |
| Investment bankers generally have to work for long hours in a highly demanding work environment. | While work environments in the private equity space can be intensive, the work-life balance is generally better because of the structured and predictable nature of the work. |
| In this case, the main focus area involves managing important financial transactions and raising capital. | Private equity firms focus on taking over companies and improving them. |

